15 Chart: Mosaic
 This chapter originated as a community contribution created by harin
This chapter originated as a community contribution created by harin
This page is a work in progress. We appreciate any input you may have. If you would like to help improve this page, consider contributing to our repo.
15.1 Overview
This section covers how to make Mosaic plots
15.2 tl;dr
library(vcd)
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
labeling = labeling_border(
abbreviate_labs = c(3, 10, 6),
rot_labels=c(0,0,-45)
),
direction=c('v','v','h'), # Age = Vertical, Music = Vertical, Favoriate = Horizonal (a.k.a DoubleDecker)
gp = gpar(fill=c('lightblue', 'gray')),
df)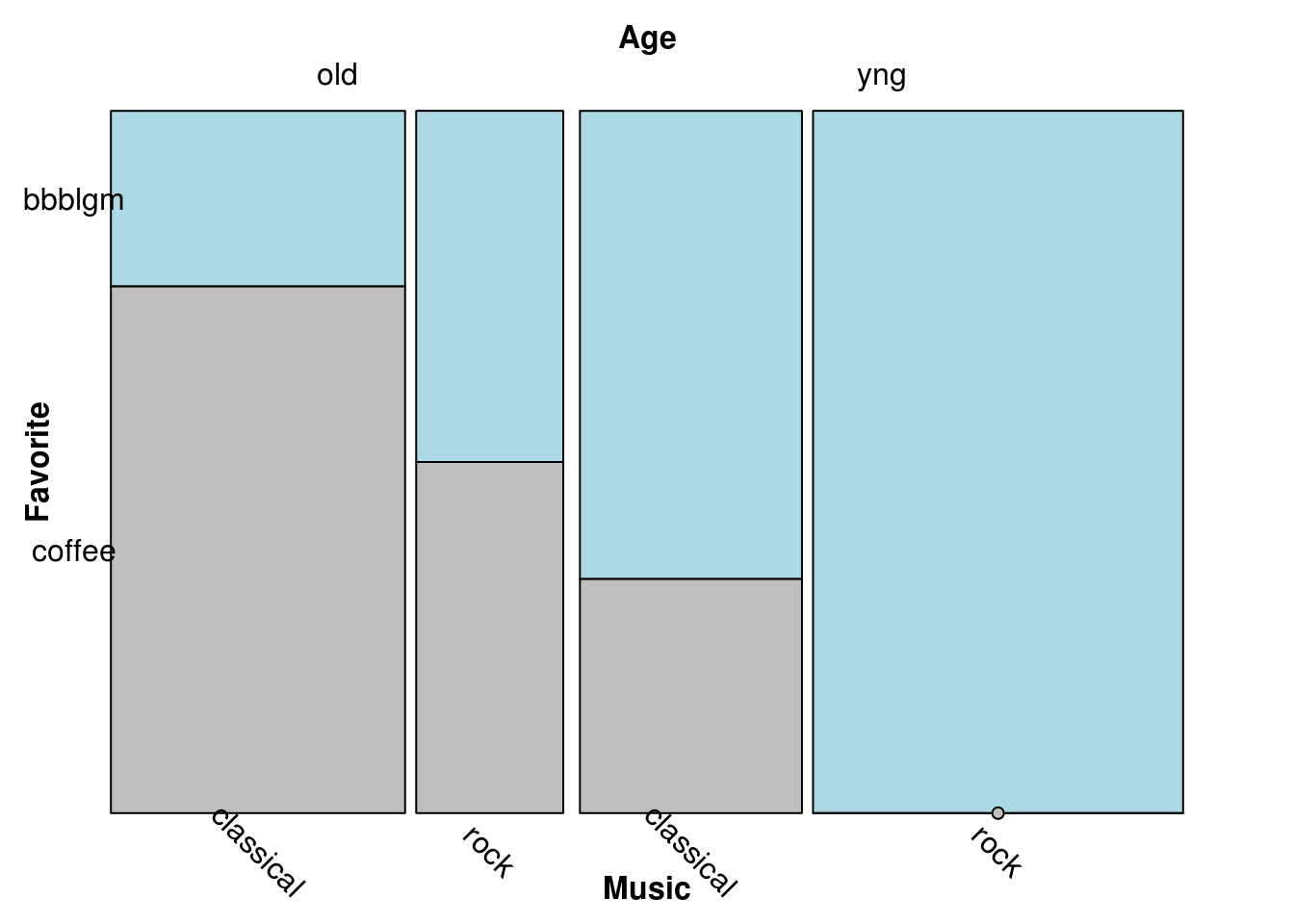
15.3 Simple Example Walkthrough
15.3.1 Order of splits
It is best to draw mosaic plots incrementally: start with splitting on one variable and then add additional variables one at a time. The full mosaic plot will have one split per variable.
Important: if your data is in a data frame (see above), the count column must be called Freq.
Split on Age only:
library(vcd)
mosaic(~Age, df)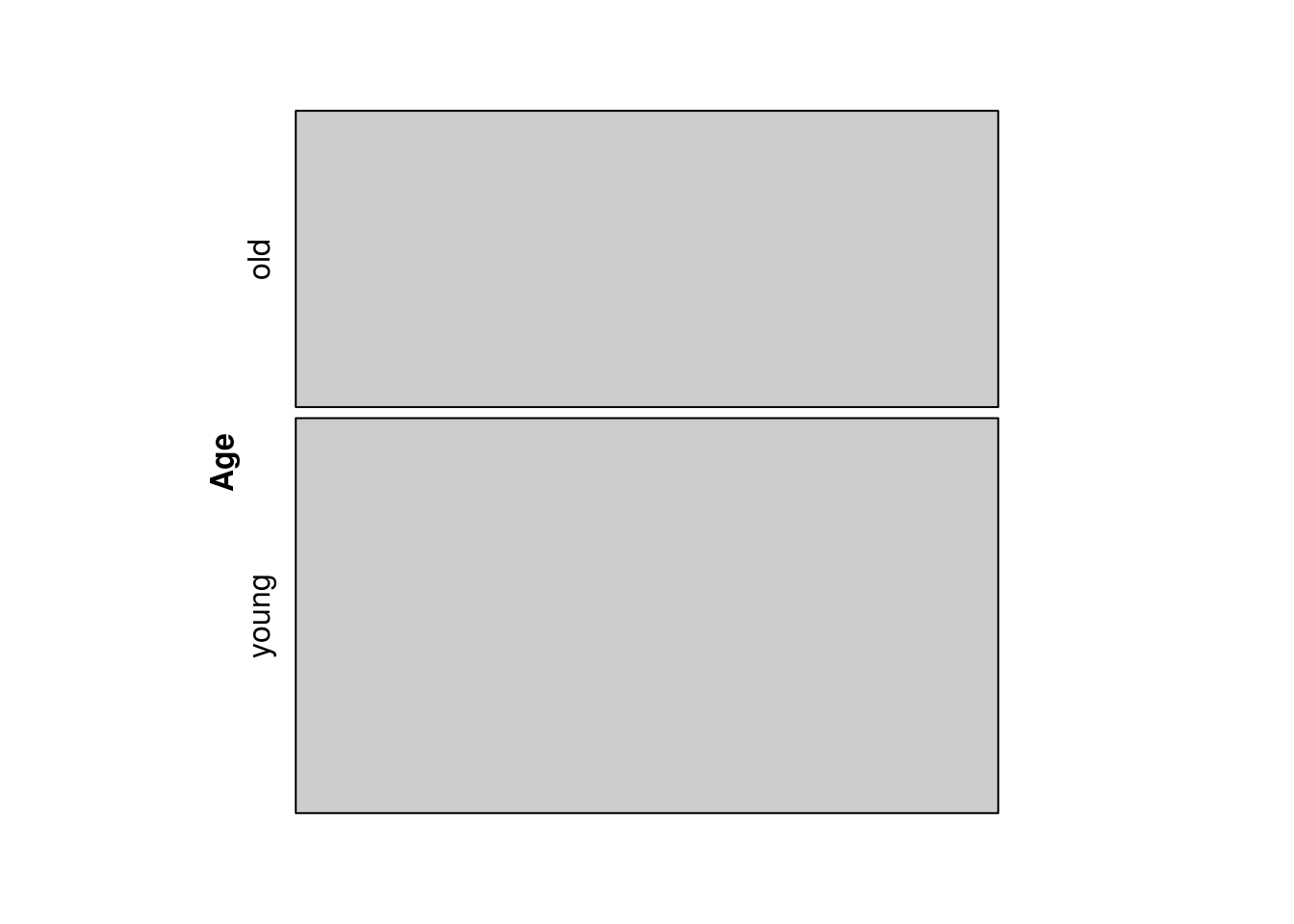
Split on Age, then Music:
mosaic(Music ~ Age, df)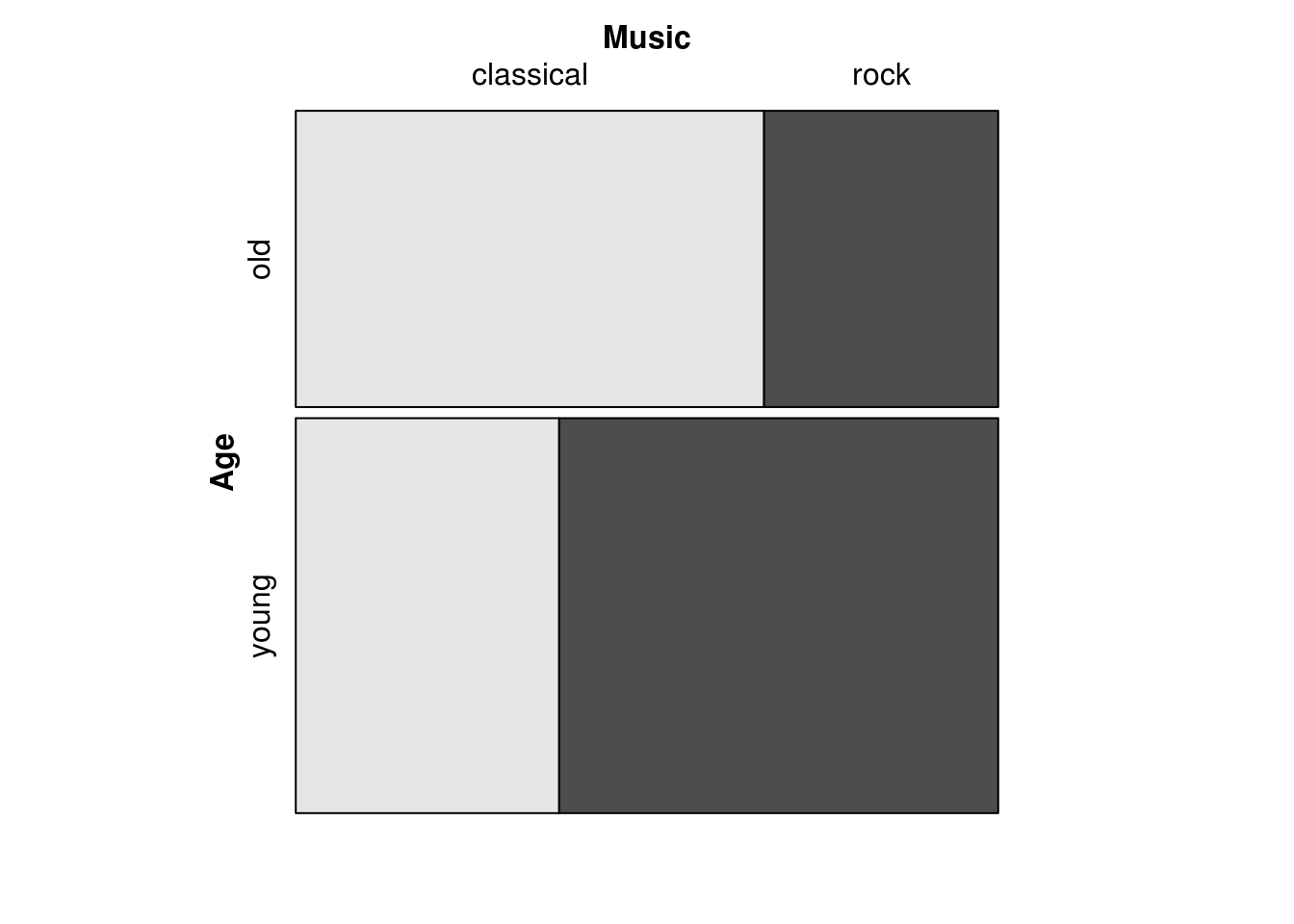
Note that the first split is between “young” and “old”, while the second set of splits divides each age group into “classical” and “rock”.
Split on Age, then Music, then Favorite:
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music, df)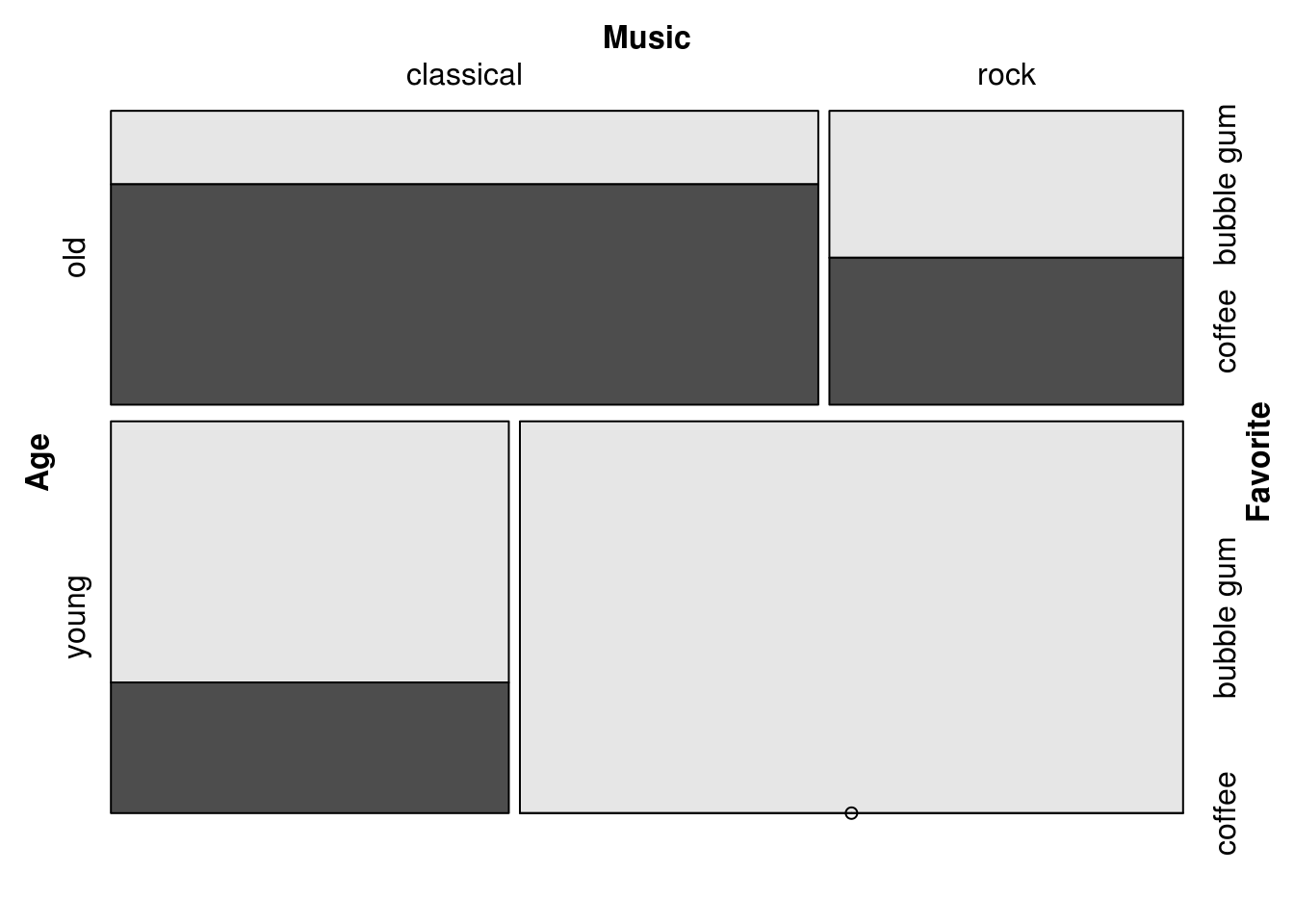
15.3.2 Direction of splits
Note that in the previous example, the direction of the splits is as follows:
Age– horizontal splitMusic– vertical splitFavorite– horizontal split
This is the default direction pattern: alternating directions beginning with horizontal. Therefore we get the same plot with the following:
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
direction = c("h", "v", "h"), df)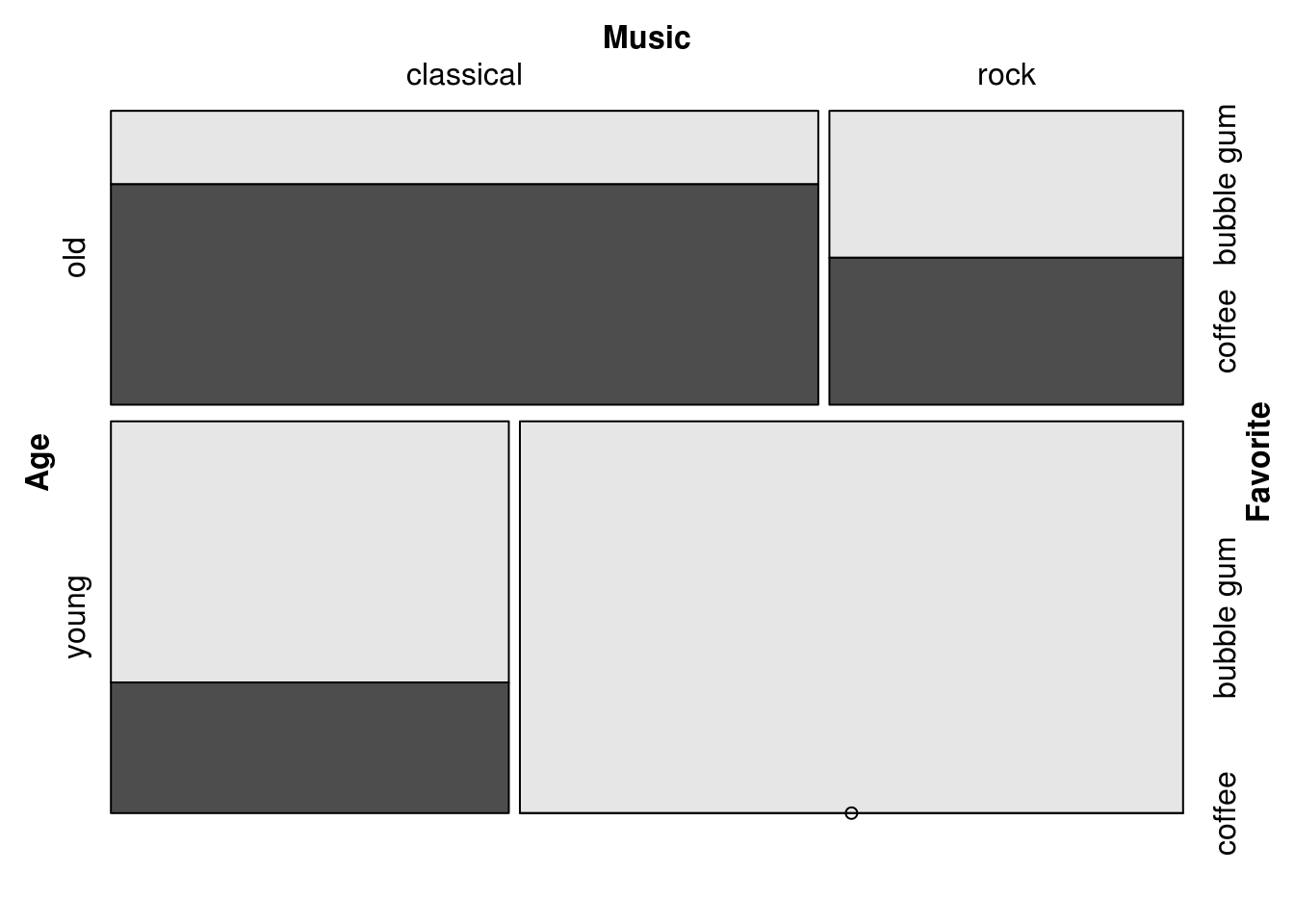
The directions can be altered as desired. For example, to create a doubledecker plot, make all splits vertical except the last one:
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
direction = c("v", "v", "h"), df)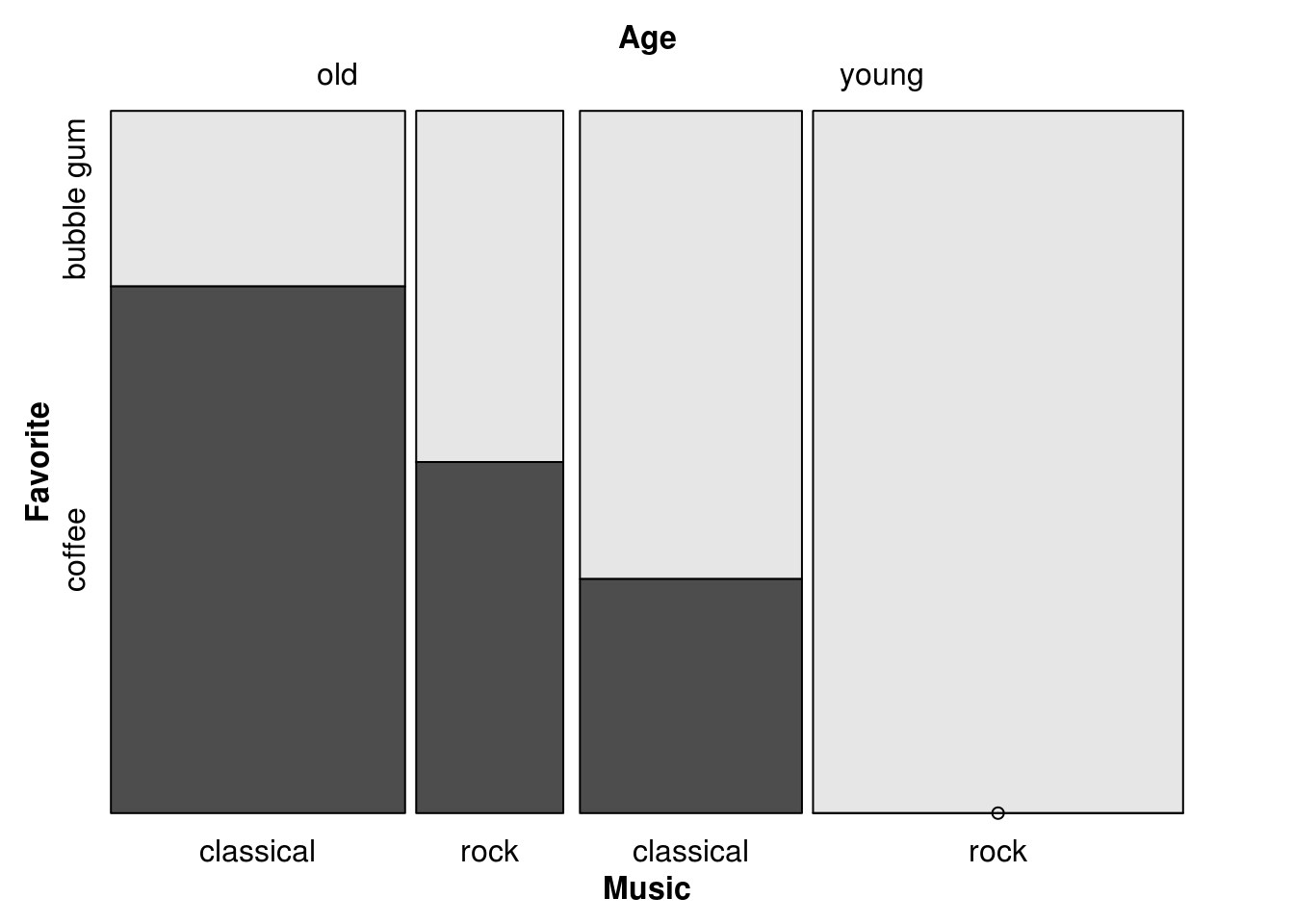
Note that the direction vector is in order of splits (Age, Music, Favorite), not in the order in which the variables appear in the formula, where the last variable to be split is listed first, before the “~”.
15.3.3 Options
15.3.3.1 Fill color:
library(grid) # needed for gpar
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
gp = gpar(fill = c("lightblue", "blue")),
df)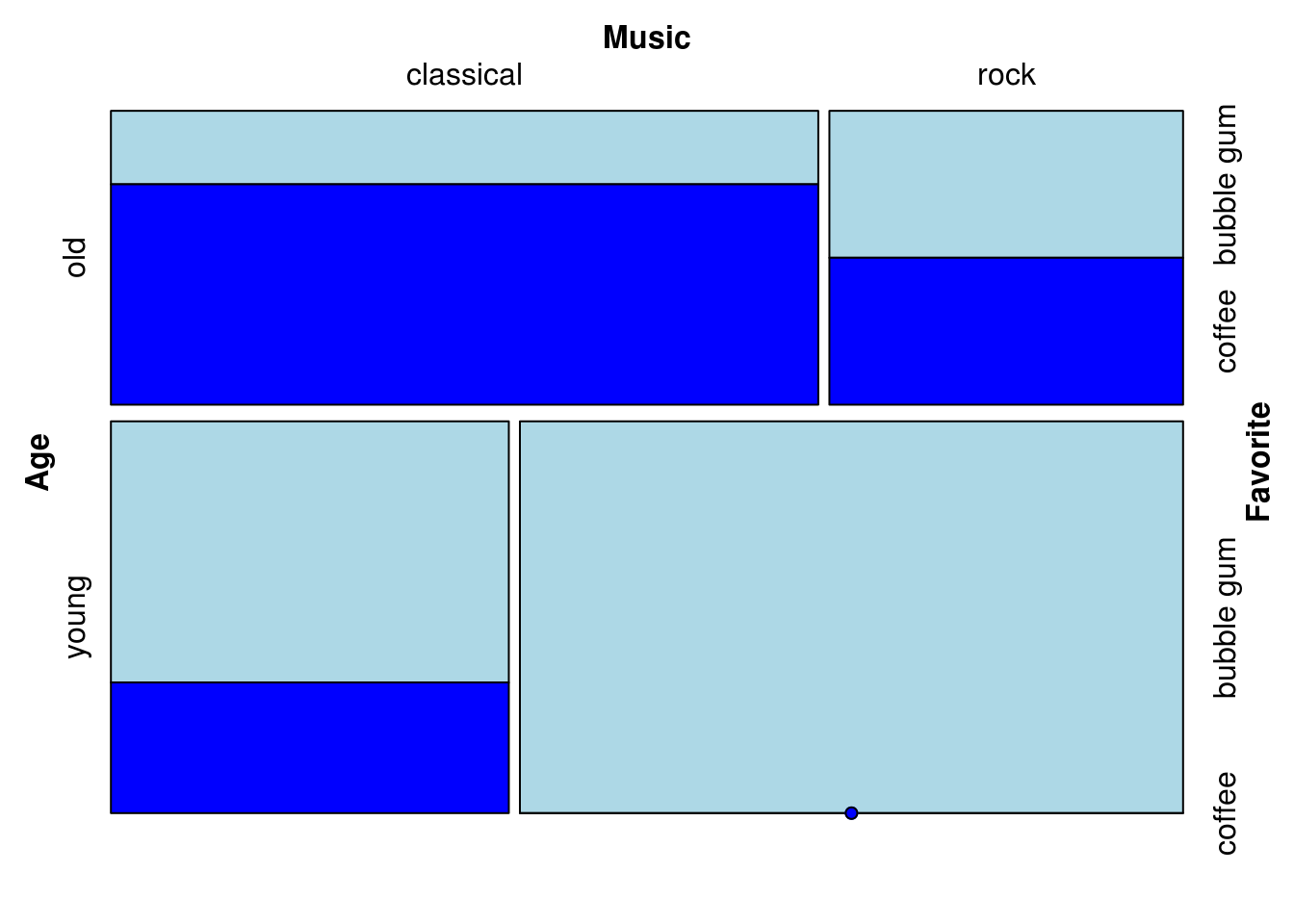
15.3.3.2 Rotate labels:
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
labeling = labeling_border(rot_labels = c(45, -45, 0, 0)),
df)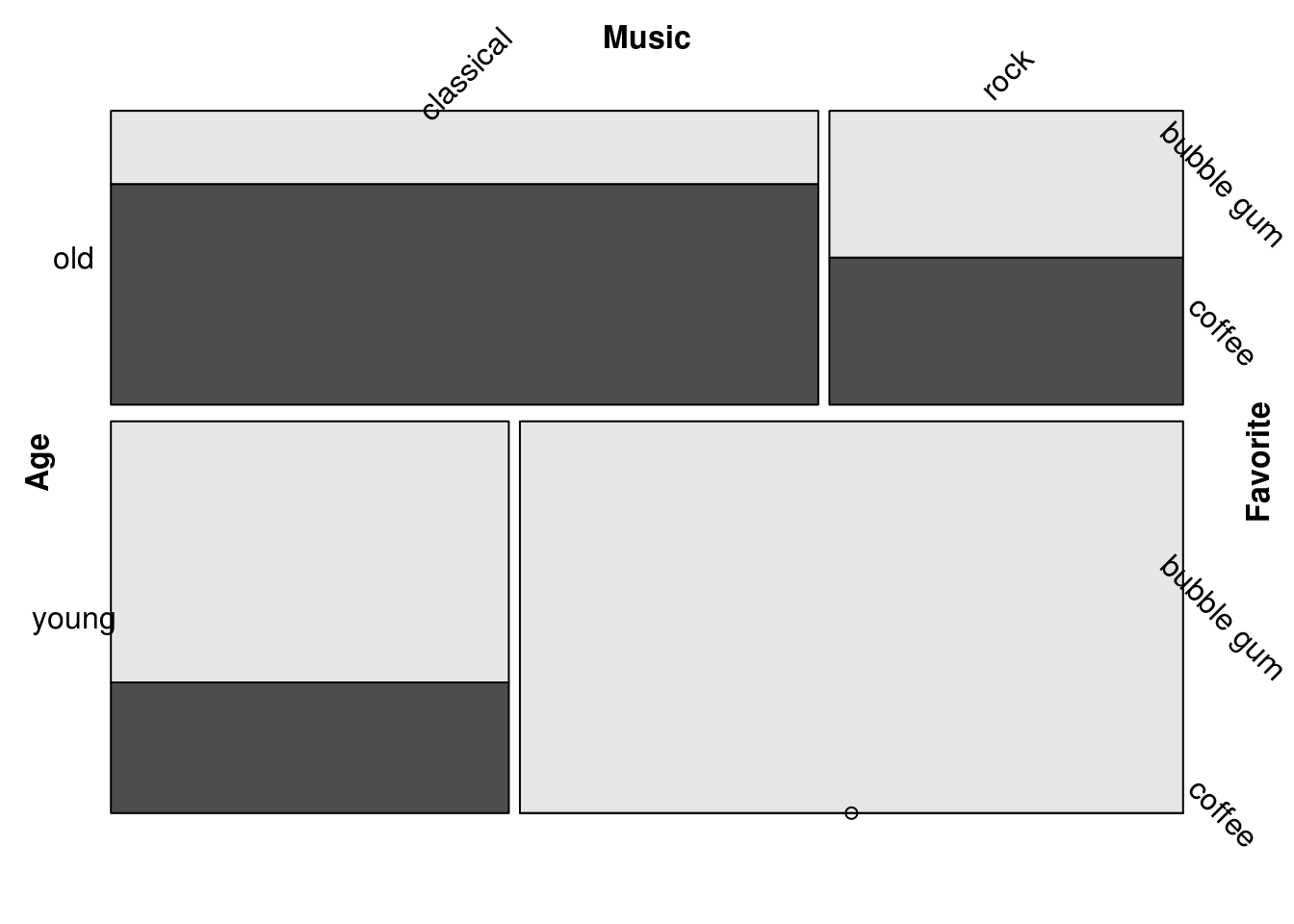
The rot_labels = vector sets the rotation in degrees on the four sides of the plot in this order: top, right, bottom, left. (Different from the typical base graphics order!) The default is rot_labels = c(0, 90, 0, 90).
15.3.3.3 Abbreviate labels:
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
labeling = labeling_border(abbreviate_labs = c(3, 1, 6)),
df)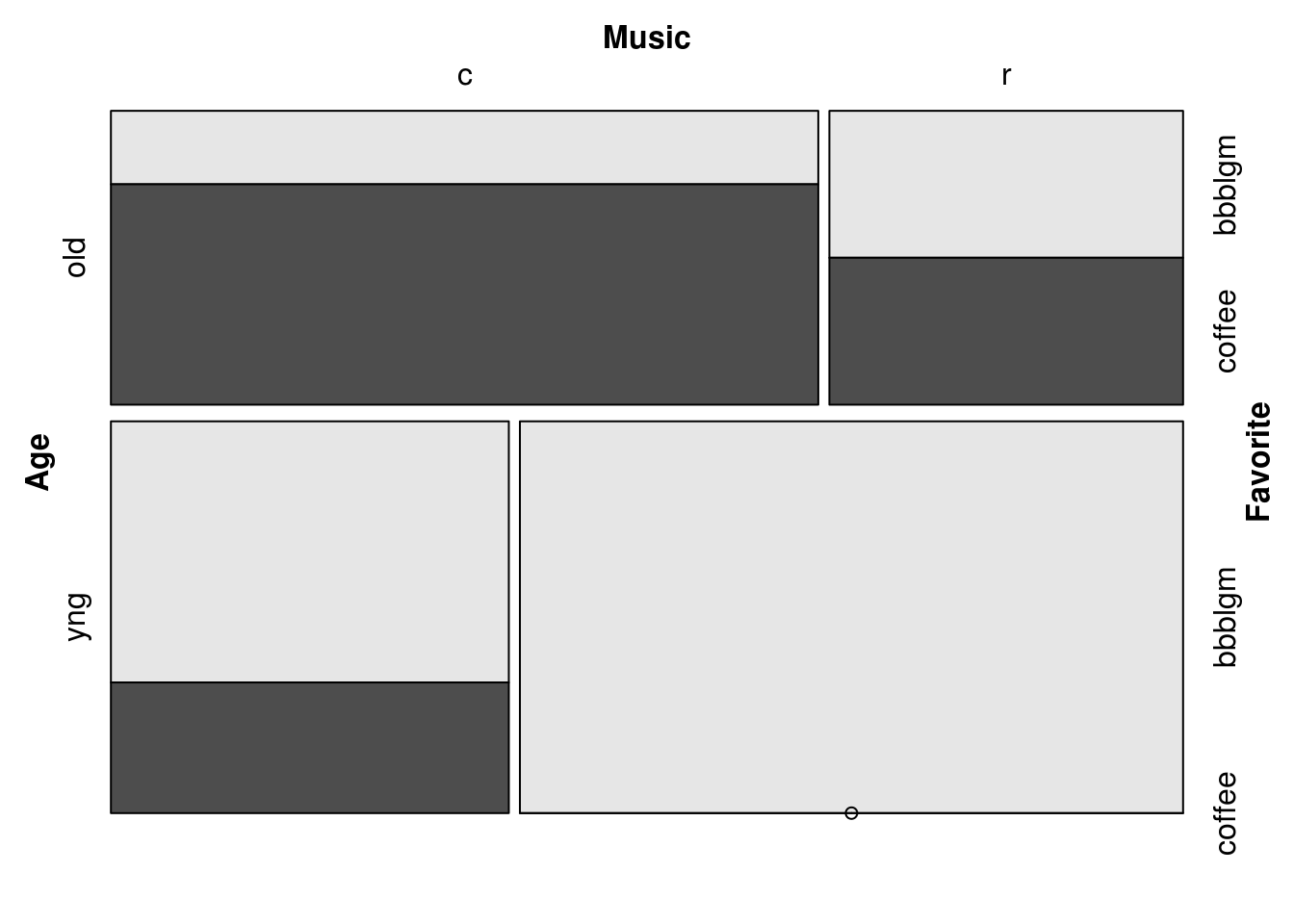
Labels are abbreviated in the order of the splits (as for direction =). The abbreviation algorithm appears to return the specified number of characters after vowels are eliminated (if necessary).
For more formatting options, see >?vcd::labeling_border.
15.3.3.4 Remove spacing between cells
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
spacing = spacing_equal(sp = unit(0, "lines")),
df)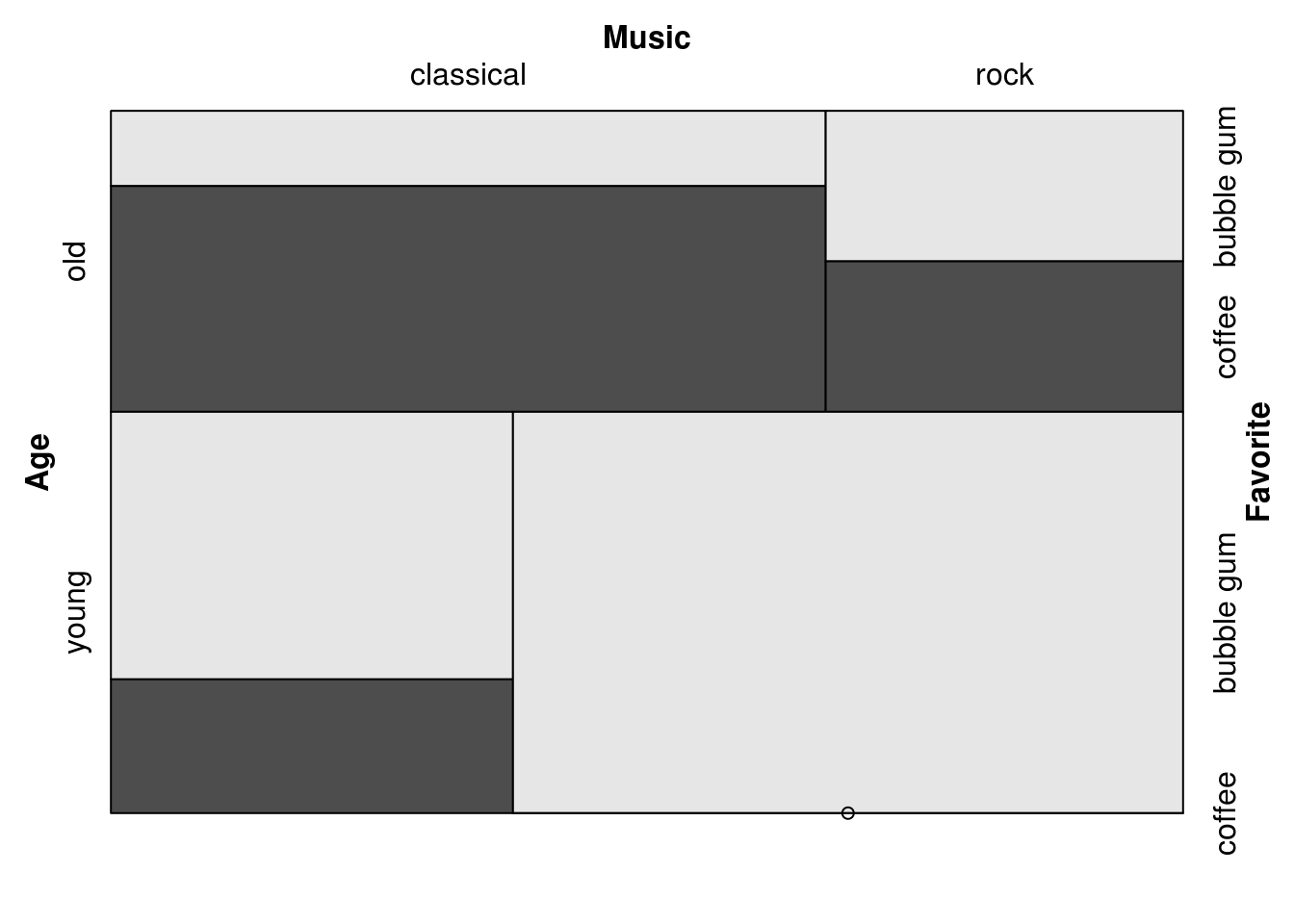
For more details, see >?vcd::spacings
15.3.3.5 Change border color (must also set fill(?))
mosaic(Favorite ~ Age + Music,
gp = gpar(fill = c("lightblue", "blue"),
col = "white"),
spacing = spacing_equal(sp = unit(0, "lines")),
df)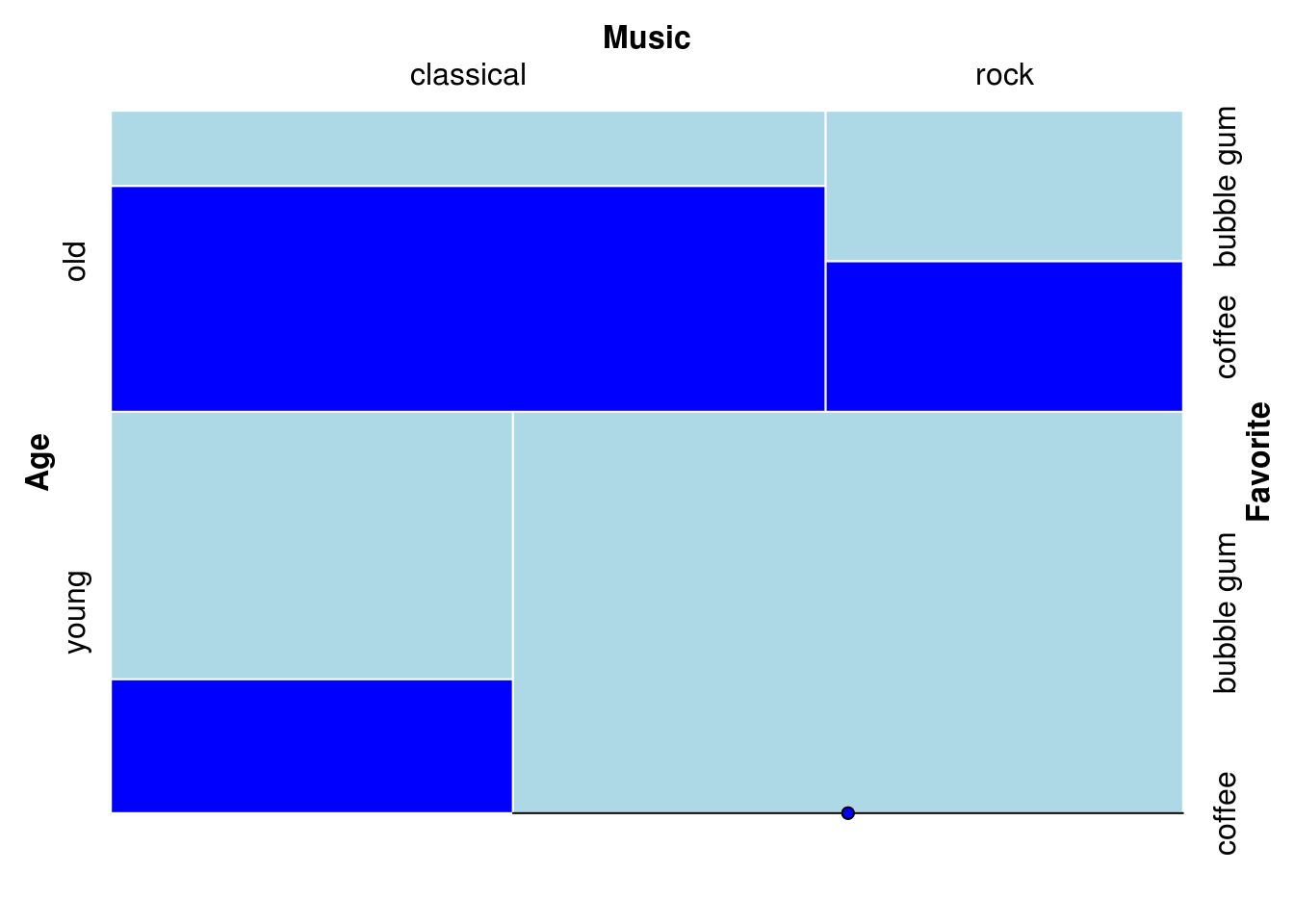
15.4 Mosaic using base R
library(vcdExtra)
mosaicplot(xtabs(count ~ lake + sex, data=Alligator), main="")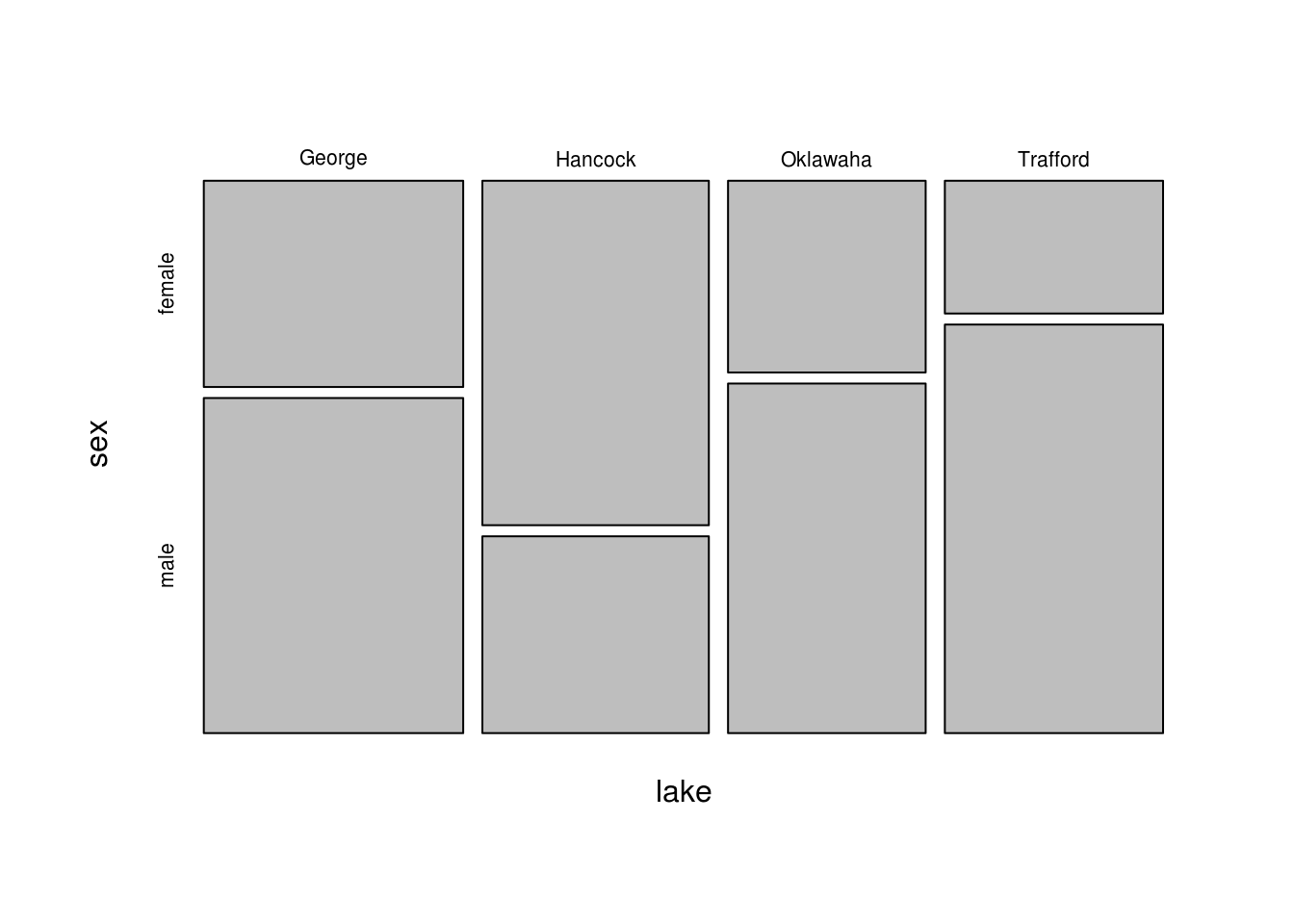
mosaicplot(xtabs(Freq ~ Favorite + Age + Music, data=df), main="",
dir=c('h', 'v', 'v'))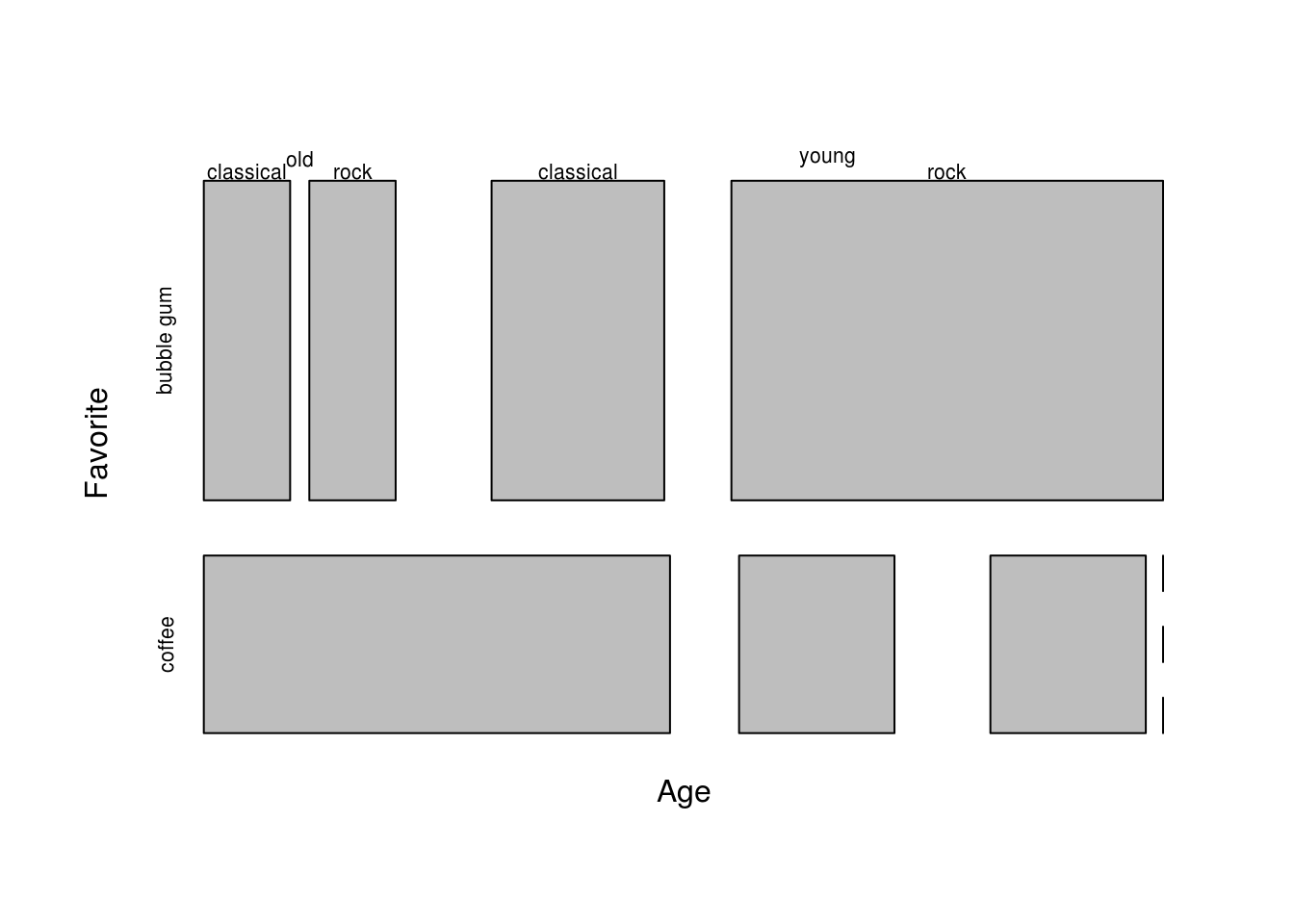
15.4.1 Mosaic using vcd::doubledecker
data(Arthritis)
vcd::doubledecker(Improved ~ Treatment + Sex, data=Arthritis)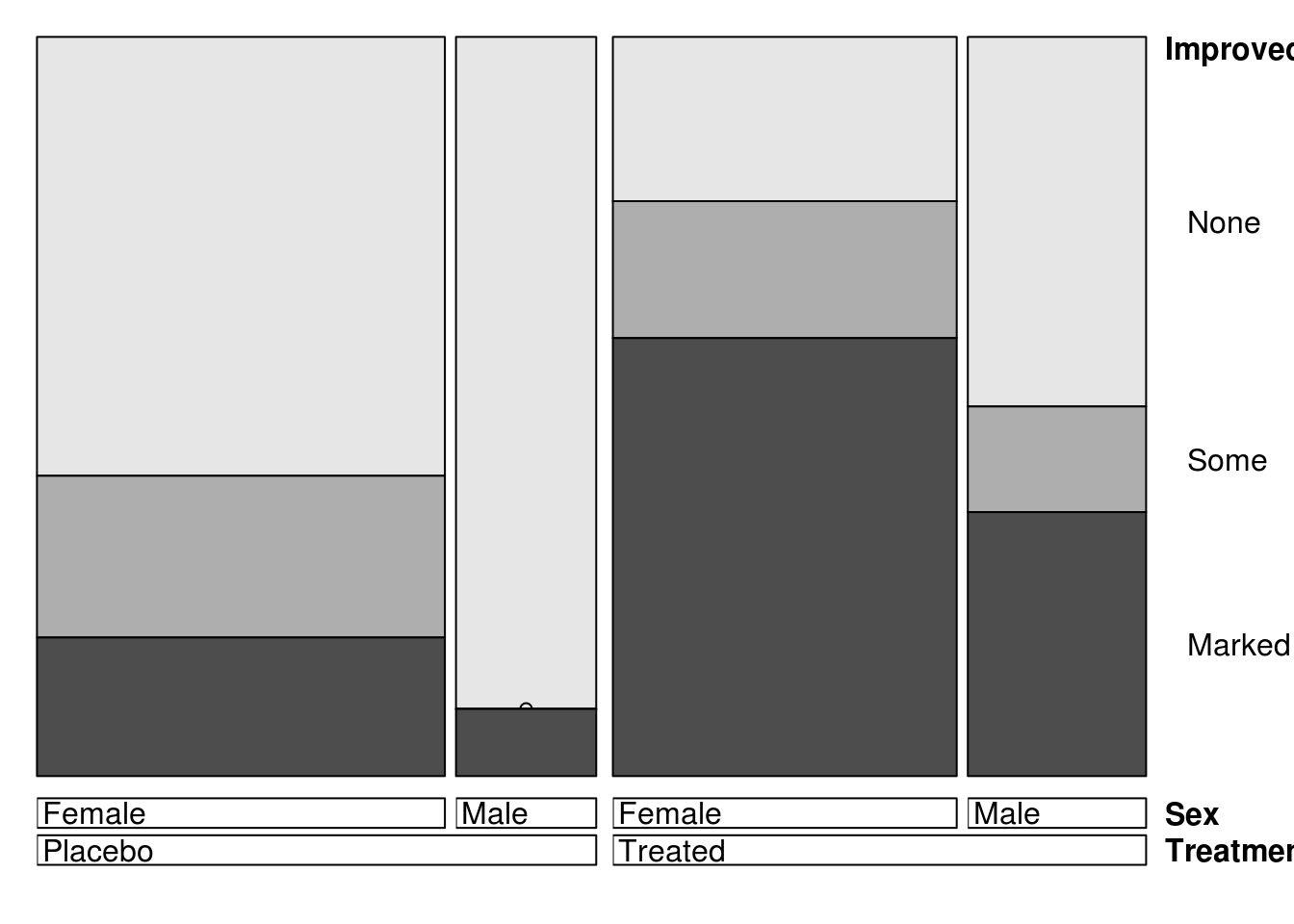
vcd::doubledecker(Music ~ Favorite + Age,
xtabs(Freq ~ Age + Music + Favorite, df))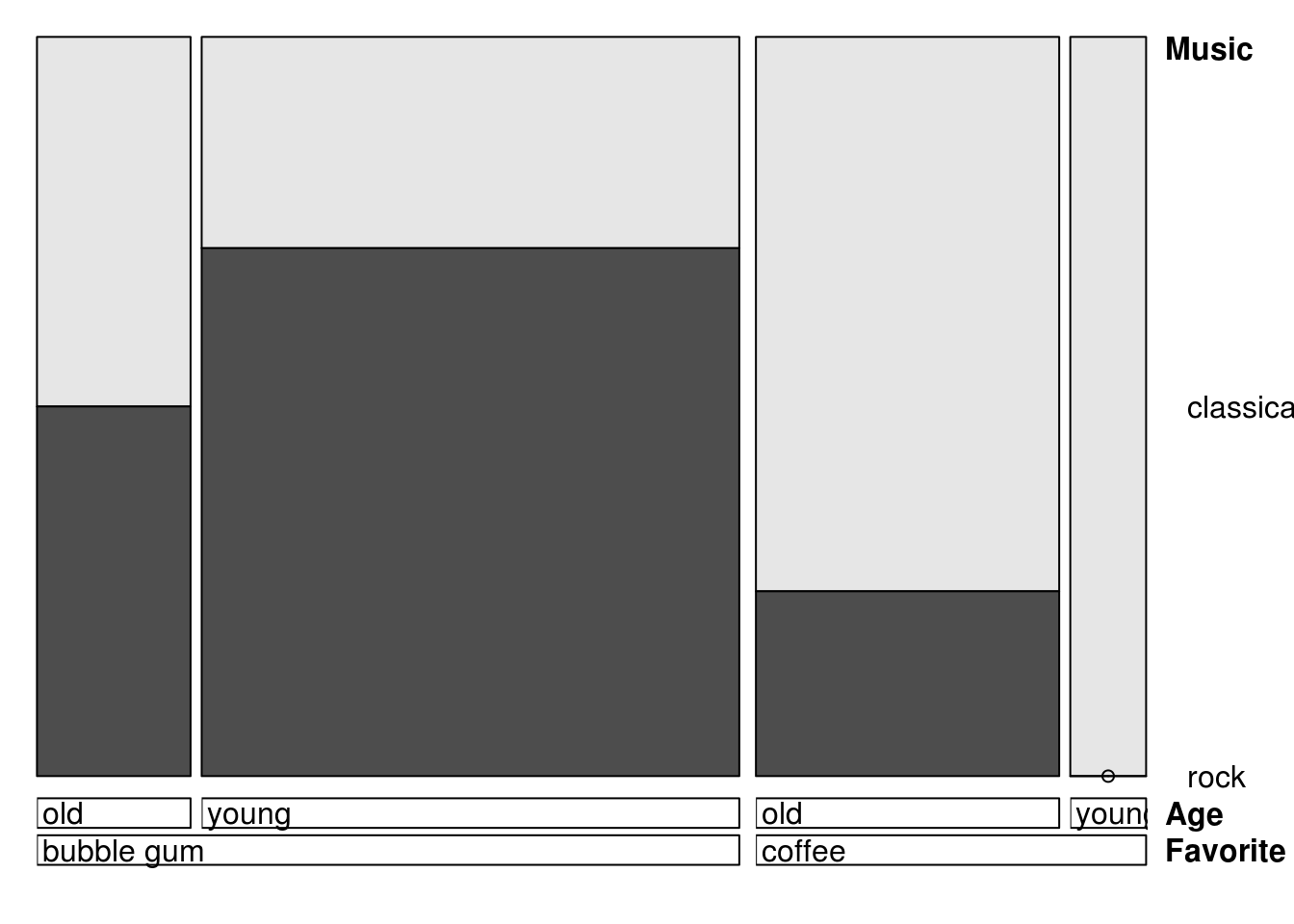
15.5 Mosaic using ggplot
For a comprehensive overview of mosaic plot in ggplot check out the link below. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggmosaic/vignettes/ggmosaic.html
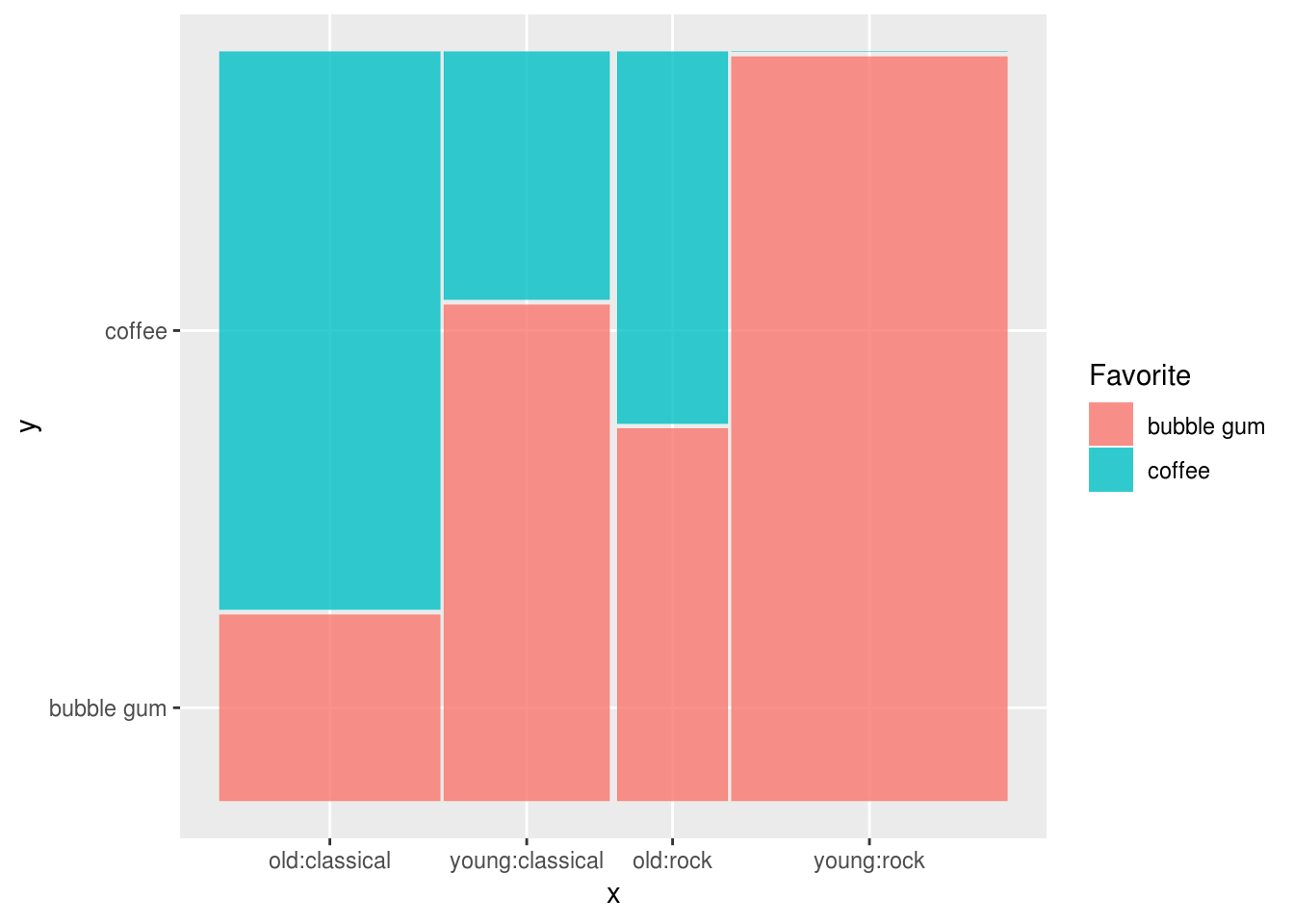
library(ggmosaic)
# equivalent to doing Favorite ~ Age + Music in vcd::mosaic with doubledecker style cut
ggplot(df) +
geom_mosaic(
aes(x=product(Favorite, Age, Music), # cut from right to left
weight=Freq,
fill=Favorite
),
divider=c("vspine" , "hspine", "hspine") # equivalent to divider=ddecker()
) 
15.6 Theory
15.7 When to use
When you want to see the relationships in Multivariate Categorical Data
15.8 Considerations
15.8.1 Labels
Legibility of the labels is problematic in mosaic plot especially when there are a lot of dimensions. This can be alleviated by - Abbreviate names - Rotating the labels
15.8.2 Aspect Ratio
- lengths are easier to judge than area, so try to use rectangles with same width or height
- Taller thinner rectangles are better (we are better at distinguishing length than area)
15.8.3 Gaps between rectangles
- No gap = most efficient
However, a gap can help improve legibility, so try out different combinations
- Can have a gap at splits
- Can Vary gap size down the hierarchy
15.8.4 Color
- good for rates in the subgroup
- displaying residual
- emphasizing particular subgroup
15.9 External resources
Chapter 7 of Graphical data analysis with R by Anthony Unwin
Link: A comprehensive overview of mosaic plot in ggplot check out the link below.
with